A Guide to Customer Service Management CRM [Benefits & FAQ]
 Updated on
Updated on
 By Bradley Kovacs
By Bradley Kovacs
Bradley Kovacs
Bradley has been passionate about technology since childhood, starting with Microsoft Flight Simulator at age six. In college, he automated his data e...
learn more
Bradley Kovacs
Bradley has been passionate about technology since childhood, starting with Microsoft Flight Simulator at age six. In college, he automated his data e...
Table of Contents
Table of Contents
Customer service is the foundation of any business and its management is the key to success.
Have you ever had a terrible customer service experience that you swore never to deal with that company again?
We've all been there, and that's why it's so crucial for organizations to invest in customer service management. On the flip side, have you ever had a unique customer service experience in which you became a lifelong patron?
That's the power of excellent customer service management.
In this article, we'll dive deep into the world of customer service management and explore what it is, why it's essential, and how you can use it to grow your business. From customer service management strategies to the benefits of customer service CRM software, we've got you covered.
Key Takeaways
- CSM vs. CXM: While Customer Service Management focuses on reactive problem-solving and efficiency, Customer Experience Management (CXM) oversees the entire proactive customer journey.
- Centralized Operations: A robust customer service management system acts as a central hub, using CRM customer relationship management software to provide a unified 360-degree view of every client interaction.
- Power of Automation: Modern IT CRM software drives efficiency through automated workflows and self-service portals, allowing teams to resolve issues faster and scale operations without increasing headcount.
- Data-Driven Service: Utilizing customer CRM analytics transforms support from a cost center into a strategic asset, enabling personalized interactions that boost loyalty and revenue.
What Is Customer Service Management?

Customer service management (CSM) is the strategic oversight of the tools, processes, and teams used to assist customers.
While a standard customer service definition and examples might simply include answering a phone call or refunding a purchase, effective management elevates these interactions into a cohesive strategy. It ensures that every touchpoint, whether through a call center, a chatbot, or a customer service knowledge base, delivers value and resolves issues efficiently.
Several key elements make up the customer service management procedure, including:
- Developing a customer service strategy
- Managing customer service operations
- Implementing knowledge management for customer service
- Managing customer service time
- Implementing customer service CRM
- Managing customer service processes
CSM aims to create a positive customer experience by providing prompt and efficient resolutions to inquiries or issues. It also involves managing patron feedback, analyzing client data, and improving customer service processes to meet market needs and expectations.
The Difference Between CSM and Customer Experience Management
It is easy to confuse customer service management with customer experience management (CXM). While they are deeply interconnected, they are not the same. To truly leverage what's CRM software capable of, one must understand the distinction between fixing a specific problem and managing the entire journey.
What is customer experience management? It is the practice of designing and reacting to customer interactions to meet or exceed their expectations, leading to greater satisfaction, loyalty, and advocacy. While CSM is often reactive (solving a problem), CXM is proactive (optimizing the journey).
Here is a breakdown of how the two concepts differ:
|
Feature |
Customer Service Management (CSM) |
Customer Experience Management (CXM) |
|
Primary Focus |
Resolving specific issues and inquiries. |
The entire customer journey and lifecycle. |
|
Nature of Interaction |
Often reactive; the customer initiates contact when they need help. |
Proactive; anticipating needs before they become issues. |
|
Goal |
Efficiency, ticket resolution, and customer satisfaction (CSAT). |
Emotional connection, brand loyalty, and Net Promoter Score (NPS). |
|
Department |
Customer Support, Help Desk, Field Service. |
Marketing, Product Design, Sales, and Support combined. |
|
Role of CRM |
Uses customer service CRM to track tickets and history. |
Uses what is a customer relationship management system to analyze data across all touchpoints. |
The Role of a Customer Service Management System
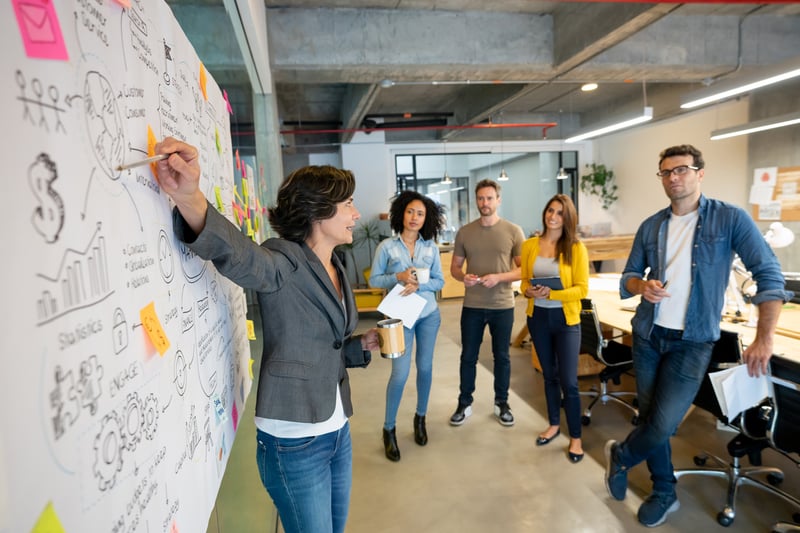

A customer service management system acts as the central nervous system for any support-focused organization. While the basic customer relationship management definition often centers on sales data, in a service context, the role shifts to continuity and problem resolution. The system serves as the bridge between the customer's problem and the company's solution.
The table below showcases the tools available on a customer services CRM system:
|
Tool |
Description |
|
Contact Management |
Stores customer contact information, including phone numbers, email addresses, and social media profiles. |
|
Lead Management |
Tracks potential clients and manages the sales pipeline. |
|
Case Management |
Manages customer support tickets and resolves issues. |
|
Reporting and Analytics |
Provides valuable insights into client behavior and helps organizations make informed decisions. |
|
Automation |
Automates routine tasks, such as sending follow-up emails, tracking customer interactions, and logging customer service interactions. |
By centralizing this data, the customer service management platform empowers teams to provide personalized, efficient support that turns a frustrated user into a loyal advocate.
How Does CRM Work for Service-Based Businesses?
For service-based companies, the product is often time, expertise, or a specific outcome. CRM for service business workflows are designed to manage these unique deliverables. Unlike CRM in sales, which tracks a deal until it closes, service CRMs track the ongoing health of the relationship.
So, what is a customer relationship management system doing in these scenarios? It is scheduling appointments, managing service level agreements (SLAs), and tracking billable hours. Whether you are using specialized IT CRM software or a general tool, the goal is to align the workforce with customer needs in real-time.
To illustrate what is CRM software examples across different sectors, here is how specific industries utilize these tools to enhance their service delivery:
|
Industry |
High-Level Use Case |
Service Application |
|
IT Service Provider |
CRM for IT service provider |
Managing helpdesk tickets, tracking hardware assets, and monitoring remote systems. It ensures technicians adhere to strict response times (SLAs) for business clients. |
|
Home Services |
CRM for home services |
Scheduling and dispatching field technicians for plumbing, HVAC, or electrical repairs. This often integrates with field service management software to track GPS locations and job status. |
|
Healthcare |
CRM in healthcare industry |
Managing patient relationships, scheduling appointments, and securely storing communication history (compliant with regulations). It helps clinics send automated reminders for check-ups or vaccinations. |
|
Automotive |
CRM in automotive industry |
Tracking vehicle service history and automating maintenance reminders. Dealerships use customer CRM software to notify owners when their specific model is due for an oil change or recall repair. |
Types of Customer Service Management

There are several types of customer service management, each with its processes, technologies, and tools.
The type of CSM a business chooses to implement depends on various factors, including the size and type of organization, client demographics, and the nature of the customer support required.
By carefully considering these factors, companies can ensure they provide their customers with the most effective and efficient customer service possible. Support teams generally utilize these channels when assisting clients:
- In-Person Customer Service - This type of CSM involves face-to-face interactions in a physical store or at a service desk. In-person customer service is ideal for organizations requiring a personal touch, such as high-end retail stores, luxury hotels, and premium banks.
- Phone Customer Service - Telephonic customer service sees customers calling a dedicated helpline to resolve their queries or issues. This is ideal for companies seeking direct communication with customers, such as telecom companies and utility providers.
- Email Customer Service - Email customer service effectively provides customer support by allowing them to communicate their concerns in writing. Businesses that receive many requests, such as online retailers, e-commerce platforms, and software providers, commonly utilize this CSM.
- Chat Customer Service - Real-time communication allows customers to chat with support representatives through instant messaging. Perfect for enterprises catering to clients who prefer quick, convenient support, such as online gaming and social media platforms.
Now, let's look at the most common types of customer service management to understand each one.
1. Customer Service Operations Management
Customer service operations management involves overseeing and managing the day-to-day activities of customer service teams. This includes managing staffing levels, scheduling, and resource allocation to ensure prompt and efficient resolution of customer requests or problems.
Effective customer service operations management focuses on continuous improvement and optimization of client service processes to increase efficiency, reduce wait times, and improve customer satisfaction.
The following describes the key components of customer service operations management:
- Service Level Agreements (SLAs) - SLAs are agreements between an organization and its customers that outline the level of service that will be provided. SLAs help set expectations for both the company and the client while providing a way to measure the performance of customer service operations.
- Process Mapping - Process mapping is documenting and analyzing customer service operations to locate areas for improvement. This includes identifying the steps involved in each process, the roles and responsibilities of customer service employees, and any bottlenecks or inefficiencies.
- Technology - Software is critical to customer service operations management. Customer service programs, such as CRM systems, can automate many aspects of customer service operations, such as ticket tracking, case management, and email responses.
- Staffing and Training - The success of customer service operations management depends on the customer service staff's knowledge. Organizations should have sufficient employee levels to meet customer demand and provide adequate training to ensure that customer service teams have the know-how to deliver high-quality support.
Customer service operations management is a critical component of effective customer service. Organizations can improve customer satisfaction by implementing efficient, effective, and responsive processes to client needs while increasing efficiency, gaining valuable data insights, and improving staff well-being.
2. Customer Service Knowledge Management

Knowledge management in customer service involves creating and maintaining a centralized repository of information and resources that customer service teams can access to resolve customer inquiries and issues.
A solid knowledge management system should include various information, such as product knowledge, service procedures, and customer service scripts. This ensures that customer support teams can access the data they need to promptly and accurately resolve client issues.
The table below highlights different components of knowledge management customer service and their advantage:
|
Component |
Advantage |
|
Data Collection |
With the correct CRM system, gathering relevant data about customers and their interactions, including call center logs, email correspondence, and online chats, becomes more straightforward. |
|
Data Storage |
Knowledge management customer service management software gives you a secure location to store all collected data, making it easily accessible to customer service representatives. |
|
Data Analysis |
Collected data is evaluated to identify trends, areas for improvement and opportunities to enhance the customer experience. |
|
Knowledge Sharing |
Easier sharing of information and best practices among customer service agents to improve overall productivity. |
|
Continuous Improvement |
The ongoing process of using data analysis to improve the customer service experience and continuously refine knowledge management processes. |
3. Customer Service Time Management
Customer service time management ensures that customer service teams can handle customer questions timeously. It involves optimizing the time and resources allocated to handling client inquiries, complaints, and requests to provide the best possible customer experience while also maintaining the efficiency and productivity of the support team.
The table below highlights key elements of knowledge management customer service:
|
Component |
Description |
|
Task Prioritization |
Determining which customer service tasks are essential and must be completed first. |
|
Time Management Tools |
Using calendars, task lists, and timers to manage time effectively and gather data. |
|
Multitasking |
Balancing the need for multitasking with the requirement for focused work on individual tasks. |
|
Delegation |
Assigning tasks to other team members for efficient customer service. |
|
Process Automation |
Automating routine tasks using software to boost productivity. |
Effective customer service time management also involves continuous optimization of customer service processes to minimize response times, streamline workflows, and create the best environment possible for the patron.
4. Customer Service Process Management
Customer service process management involves designing, implementing, and refining the processes and systems used to deliver customer service. This includes developing standard operating procedures, setting client service standards, and tracking performance.
The following describes each stage of the customer service management process:
- Process Definition - This involves identifying the steps required to deliver exceptional customer service and documenting them concisely. With this, all customer service representatives understand the process and can provide consistent service.
- Process Mapping - Creating a visual representation of the customer service process aids in identifying improvement areas and can be utilized to develop new procedures or optimize existing ones.
- Process Standardization - Process guidelines ensure customer service processes are consistent and efficient. Teams can increase productivity by implementing process standardization, providing training, and using technology to automate routine tasks.
- Continuous Process Improvement - Continuous process improvement requires regularly reviewing and modifying customer service processes to keep things running smoothly. This can be accomplished through data analysis, customer feedback, and process audits.
Effective customer service process management assists customer service representatives in providing high-quality service.
Organizations can improve customer satisfaction, increase efficiency, gain valuable data insights, boost staff morale, and ensure consistent service by defining, mapping, standardizing, and improving customer service.
5. Customer Service Automation
Customer service automation is a critical component of modern customer service management. It involves using technology to perform repetitive tasks without human intervention, allowing support agents to focus on complex, high-value interactions.
When businesses ask what is CRM software used for, automation is often the primary benefit cited for scaling operations efficiently.
Key aspects of automation include:
- Self-Service Portals: Utilizing a robust customer service knowledge base allows the CRM customer to find answers instantly, significantly reducing ticket volume.
- Chatbots and AI: These tools handle initial inquiries and FAQs, instantly logging interaction data into the customer service CRM to ensure seamless handoffs to human agents if needed.
- Automated Workflows: Advanced IT CRM software can automatically route tickets to the correct department based on urgency or keywords, ensuring the customer service management system operates with speed and precision.
By integrating automation, businesses elevate their CRM customer service and support, ensuring faster resolution times and a consistent experience across all channels.
Benefits of CRM Customer Service

Implementing a robust strategy goes beyond the basic customer service definition and examples of answering phones. It transforms support into a competitive advantage.
By leveraging CRM customer relationship management software, businesses gain a comprehensive toolset that benefits both the agent and the customer.
1. Unified Customer History
A primary benefit of what is a customer relationship management system is the "360-degree view." This feature allows support professionals to see every interaction a CRM customer has had with the brand, past purchases, open tickets, and even email click-throughs, on a single screen.
Instead of asking "Can you verify your last order?", the agent can say, "I see you received your shipment last Tuesday." This context is vital. In fact, 74% of users report that their CRM system gave them improved access to customer data, significantly reducing friction during calls.
2. Automated Workflows
Speed is the currency of modern service. A customer service management system utilizes automation to bridge the gap between inquiry and resolution.
For instance, what does CRM mean in marketing contexts often involves automated drip campaigns. In service, this translates to auto-responders that acknowledge a ticket instantly or route complex technical issues directly to Tier 2 support.
By automating these repetitive tasks, CRM customer service tools can free up a significant amount of a team's time, allowing them to focus on high-value problem solving rather than data entry.
3. Improved Personalization
Customers expect brands to know them, and a CRM in business is the engine that drives this personalization. By analyzing customer CRM software data, such as birthdays, location, and preferred products, companies can tailor every communication.
This extends to Account-Based Marketing (ABM), where key high-value clients receive white-glove service. Statistics show that personalization can drive a revenue uplift of 10-15%, proving that using data to treat people like individuals rather than numbers pays off.
4. Scalable Client Management
As a business grows, spreadsheets break. CRM customer relationship management software is built to handle volume, allowing you to manage thousands of contacts without losing track of a single conversation.
Whether you are a small startup or a large enterprise, CRM for service business tools scale with you. Research indicates that 65% of small-to-medium businesses adopt a CRM within their first five years to manage this critical transition from ad-hoc contact lists to a centralized database.
5. Actionable Analytics
What is CRM software used for if not to learn from your own performance? Marketing CRM and service modules provide actionable analytics, such as average response time, customer satisfaction scores (CSAT), and ticket volume trends.
These insights allow managers to spot bottlenecks, like a surge in returns on a specific product, and fix them at the source. The financial impact is clear: the average return on investment for CRM technology is roughly $8.71 for every dollar spent.
6. 24/7 Accessibility
Modern service doesn't happen just at a desk. IT CRM software now comes with robust mobile applications, allowing field technicians and sales reps to access real-time data from anywhere. This "service on the go" capability is a game-changer for efficiency.
Sales and service professionals using mobile CRM apps are approximately 65% more likely to meet their quotas than those using non-mobile solutions, ensuring that the customer service knowledge base and client history are always in their pocket.
FAQs
What Is Customer Engagement CRM?
Customer engagement CRM is a type of CRM that focuses on improving customer interactions and building stronger relationships. It is designed to help companies understand customer behavior and preferences and use that information to personalize communications or marketing.
What Is Customer Service Management in Retail?
Customer service management in retail is managing customer interactions and experiences in a retail setting. It involves everything from managing customer service operations and processes to training agents and tracking customer satisfaction.
What Is Customer Service Management Strategy?
A customer service management strategy is a plan for managing customer interactions and experiences. It outlines the goals, objectives, tactics, and processes that customer service teams utilize to achieve the desired results. A customer service management strategy is essential to serving your client better.
Is CSM the Same as CRM?
No, but they are closely related. CRM is the broader strategy and technology used to manage an organization's interactions with potential and existing customers across sales, marketing, and support.
Customer Service Management is a specific discipline within that ecosystem. It focuses exclusively on the operations, workflows, and strategies of the support department.
Think of it this way. CRM customer relationship management software is the house, and CSM is a specific room within that house (the service department).
What is the "10 5 3" Rule in Customer Service?
The "10-5-3" rule is a popular hospitality and retail guideline used to ensure every customer feels acknowledged based on their physical proximity to a staff member. It helps field teams (like those using field service management software) and retail staff maintain a welcoming atmosphere.
- 10 Feet: When a customer is 10 feet away, acknowledge them with eye contact and a warm nod.
- 5 Feet: When they are 5 feet away, smile and offer a verbal greeting (e.g., "Hello," "Welcome").
- 3 Feet: (In some variations) When within 3 feet, engage them with a specific offer of help or conversation.
This rule transforms a passive customer service definition and examples into a proactive engagement strategy.
Customer Service Management - Final Thoughts
Customer service management is critical for any business wanting to provide excellent customer experiences and build solid client relationships. Whether you want to improve customer satisfaction, increase sales, or simply streamline your customer service operations, CRM software is an effective tool to help achieve these goals.
With its ability to automate routine tasks, provide valuable insights into customer behavior, and improve collaboration among agents, CRM platforms are an integral part of a successful customer service management strategy.
Remember, the key to success in customer service management is to focus on providing an excellent customer experience. You can build strong customer relationships and drive long-term business success by putting clients first and using tools like Ringy to support your efforts.
Take the first step towards improving your customer service management today.
Request a demo to learn how Ringy can help you to achieve your customer service goals.

Skyrocket your sales with the CRM that does it all.
Calling? Check. SMS? Check. Automation and AI? Check. Effortlessly keep in touch with your customers and boost your revenue without limits.

Take your sales to new heights with Ringy.
Sales in a slump? Ringy gives you the tools and flexibility you need to capture leads, engage with them, and turn them into customers.
Subscribe to Our Blog
Enter your email to get the latest updates sent straight to your inbox!
Categories
Related Articles