STP Marketing Explained: Model, Strategy, and Real-World Examples
 Updated on
Updated on
 By Carlos Correa
By Carlos Correa
Carlos Correa
Carlos has been involved in the sales space for well over ten years. He began in the insurance space as an individual sales agent, managing teams as s...
learn more
Carlos Correa
Carlos has been involved in the sales space for well over ten years. He began in the insurance space as an individual sales agent, managing teams as s...
Table of Contents
Table of Contents
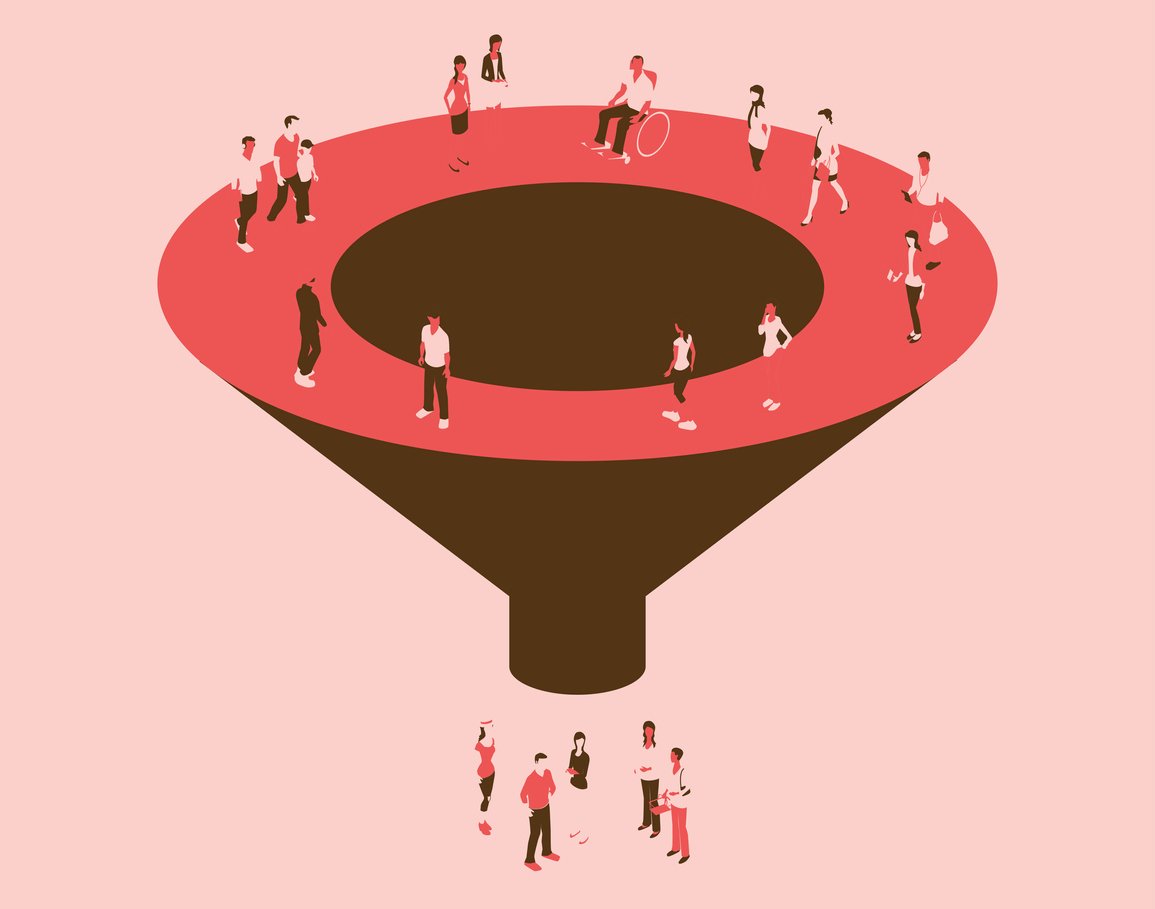
Marketing is about reaching the right people. That's where STP marketing comes in. It's a simple framework—Segmentation, Targeting, and Positioning, but it has a massive impact on how brands craft their message and connect with their ideal customers.
Instead of casting a wide net and hoping something sticks, the STP model helps marketers get specific. It's about understanding your audience, narrowing your focus, and making sure your product or service stands out in a way that matters.
The result? Smarter campaigns, better engagement, and more efficient use of your budget.
In this guide, we'll break down what STP means in marketing, why it works, and how to use it. Whether you're new to the concept or just need a refresh, you're in the right place.
Let's get into it.
What Is STP in Marketing?

STP in marketing is a strategic approach that helps businesses connect with the right audience by breaking down a broad market into manageable, targeted chunks.
Instead of shouting your message into the void and hoping it lands, STP marketing lets you tailor your brand's voice to the people who actually want to hear it.
At its core, STP marketing stands for Segmentation, Targeting, and Positioning, a model that shifts the focus from product-centered marketing to customer-centered strategy. It's about understanding who your customers are, what they care about, and how to speak to them in a way that makes them choose you over everyone else.
STP Marketing Definition
The STP marketing model is a three-step process that starts with dividing the market (segmentation), selecting your ideal customers (targeting), and then crafting a clear brand message that positions your product as the best solution (positioning).
It's simple in theory, but incredibly powerful in practice, especially when backed by tools like Ringy, which lets you organize customer data, automate follow-ups, and personalize communication at scale.
What Does STP Mean in Marketing?
STP in marketing means moving from product-pushing to customer-focused messaging. Instead of asking, "How can we sell more?" the STP mindset prompts better questions like:
- Who are we really trying to help?
- What exactly are their problems?
- Why should they care about us over anyone else?
In other words, STP means marketing with precision and purpose. It forces you to stop treating your audience as a monolith and start seeing the specific challenges, preferences, and motivations that drive different groups.
Here's what it changes in practice:
- Your campaigns become tighter. You're no longer trying to speak to everyone, you're speaking clearly to someone.
- Your messaging becomes more specific. No more vague taglines. You talk like you understand their world—because you do.
- Your offers become more appealing. When a customer feels like the solution was made for them, they're far more likely to say yes.
Example in action: If you're using Ringy and you know your segment is time-strapped real estate agents, you're not sending generic CRM emails. You're running a campaign titled "Close listings faster—without chasing leads." You're using SMS automation and pre-set follow-ups to match how they actually work.
That's what STP means when it comes to action—it informs every decision, from product packaging to subject lines.
STP Meaning in Marketing and Why It Matters
The meaning of STP in marketing goes beyond just identifying customers. It's about relevance. Relevance is everything in today's saturated digital landscape because consumers are bombarded with offers, ads, and content every second.
If you're not speaking directly to their needs, they'll scroll right past you. STP gives you the framework to make your marketing relevant, which is how you build loyalty, boost conversions, and reduce wasted ad spend.
STP Marketing Model Breakdown
The STP marketing model is the big-picture framework. It's about understanding the flow of decision-making from identifying market opportunities to creating tailored brand messages. Think of this as the strategy map that guides your entire marketing approach.
This breakdown focuses on the process and how it fits into your overall strategy:
|
Process |
Description |
|
1. Conduct Market Research |
Understand your total addressable market, buyer behaviors, and emerging trends. |
|
2. Segment the Market |
Group potential customers based on shared characteristics, demographics, psychographics, behavior, or needs. |
|
3. Evaluate and Select Target Segments |
Look at profitability, competition, and alignment with your product strengths. |
|
4. Develop Positioning Strategy |
Decide how you'll stand out in the eyes of your chosen segment. |
|
5. Align Product, Messaging, and Channels |
Tailor your product offering, marketing language, and platforms to fit the audience you're targeting. |
As you can see, The STP model is all about strategy design. It's the blueprint that keeps your marketing aligned with business goals.
What Does STP Stand For in Marketing?

If you're still wondering, what does STP stand for in marketing?—let's break it down, simply and clearly. STP is an acronym for Segmentation, Targeting, and Positioning. These are the building blocks of a strong marketing strategy, and each step plays a key role in helping you speak to the right people in the right way.
1. Segmentation
Segmentation is the first step in understanding your audience. It involves splitting the broader market into smaller, more defined groups based on shared characteristics.
Common audience segmentation categories:
- Demographics: Age, gender, income, education
- Geographics: Country, city, climate
- Psychographics: Lifestyle, personality, values
- Behavioral: Purchasing habits, brand interactions, product usage
Example: A fitness app might segment users by fitness goal, weight loss, muscle gain, or general wellness—since each group has distinct motivations and engagement patterns.
2. Targeting
Once you've segmented your audience, targeting is about selecting the group(s) that are most viable and valuable for your business. Not every segment is worth pursuing, so targeting helps you focus your resources where they'll have the most impact.
Targeting approaches:
- Broad (undifferentiated): Same message to everyone
- Segmented (differentiated): Different messages to different segments
- Niche (concentrated): Focused effort on a single segment
- Micromarketing: Personalized marketing down to individual customers or neighborhoods
Example: A budget airline may target price-sensitive travelers who prioritize low fares over luxury, rather than trying to attract business-class flyers.
3. Positioning
Positioning is how you craft your product's image in the minds of your target audience. It's not just what you offer, it's how you want people to perceive you compared to alternatives.
Effective positioning is:
- Clear: No confusion about what you do or who you serve
- Relevant: Speaks directly to your segment's needs or problems
- Differentiated: Highlights what sets you apart from competitors
Example: A plant-based meal delivery brand might position itself as the eco-conscious, health-first option for busy professionals who don't want to compromise on quality or ethics.
The STP Process in Marketing

The STP process in marketing brings structure to how businesses identify their audience, craft targeted messages, and position their brand effectively.
It takes the guesswork out of campaigns and replaces it with a data-driven, customer-centric approach that improves engagement and conversions.
Here's how it works in practice.
Step-by-Step Breakdown of the STP Process Marketing Teams Use
The STP process unfolds in three key stages. Each one builds on the last to ensure that your campaigns aren't just creative, they're strategically aligned with audience needs.
- Segmentation: Analyze the broader market and break it down into meaningful customer groups. These groups should share common traits that influence their buying decisions, such as age, income, lifestyle, or purchase behavior. Use customer data, surveys, analytics tools, or CRM insights to identify these segments.
- Targeting: Once your segments are defined, evaluate which ones are most aligned with your business objectives. This might involve looking at segment size, growth potential, accessibility, or how well your product solves their specific problems. You don't have to target every group, just the ones with the most potential.
- Positioning: With a segment (or a few) selected, it's time to shape your messaging. Positioning is about defining how you want that audience to perceive your product or brand. It includes developing a value proposition that speaks directly to their needs and differentiates you from the competition.
How to Use STP in Marketing Campaigns
Here's a quick look at how the STP framework plays out when applied directly to a marketing campaign:
|
Step |
Description |
Example |
|
Segmentation |
Dividing the market by criteria |
Age, income, location |
|
Targeting |
Selecting the best-fit segments |
Young professionals in cities |
|
Positioning |
Creating a clear brand message |
"Affordable luxury for busy lives" |
Let's say you're launching a line of eco-friendly work bags. Using the STP model:
- You segment your audience by age, income, job role, and sustainability values.
- You target urban professionals aged 25–35 who value minimalist design and ethical manufacturing.
- You position your product as a stylish yet responsible choice for the eco-conscious commuter.
This structure not only sharpens your campaign focus, but also helps your message feel personalized—because it is.
Importance of STP in Marketing

The STP model enables marketers to craft messages that resonate with specific audiences, leading to more efficient and impactful campaigns. Le't's explain how that happens.
Why STP is Essential for Marketing Effectiveness
The STP model allows businesses to:
- Identify and Understand Distinct Customer Segments: By segmenting the market, companies can recognize the unique needs and preferences of different groups.
- Target the Most Valuable Segments: Focusing on segments that align closely with the company's offerings ensures better resource allocation and higher conversion rates.
- Position Their Brand Effectively: Crafting a clear and compelling brand message that appeals to the targeted segment enhances brand perception and loyalty.
This strategic approach ensures that marketing efforts are not only efficient but also yield better results by addressing the specific needs of the audience.
Benefits of Using the STP Marketing Strategy
Implementing the STP model offers several advantages:
- Focused Messaging: Tailoring messages to specific segments ensures relevance and increases engagement.
- Better ROI: By concentrating efforts on the most promising segments, companies can achieve higher returns on their marketing investments.
- Stronger Brand Positioning: A well-defined position in the market differentiates the brand and fosters customer loyalty.
STP Marketing Strategy in Action
Let's see how companies analyze, build, and implement STP strategies effectively.
STP Marketing Analysis Techniques
Companies employ various techniques to analyze and segment their markets:
- Data Analysis: Utilizing customer data to identify patterns and segment the market based on demographics, behavior, and preferences.
- Market Research: Conducting surveys and focus groups to gain insights into customer needs and perceptions.
- Competitive Analysis: Understanding competitors' positioning to identify market gaps and opportunities.
These techniques enable businesses to make informed decisions about which segments to target and how to position their offerings.
How Companies Build Campaigns Using STP
Once the analysis is complete, companies proceed to:
- Develop Targeted Campaigns: Crafting messages and offers tailored to the selected segments.
- Select Appropriate Channels: Choosing the most effective platforms to reach the target audience, such as social media, email, or traditional advertising.
- Monitor and Adjust: Tracking campaign performance and making necessary adjustments to optimize results.
This structured approach ensures that marketing efforts are aligned with customer needs and business objectives.
STP Marketing Meaning in Real-World Applications
The STP marketing model is a versatile framework that businesses across various industries employ to tailor their marketing strategies effectively. Here's how it manifests in different sectors:
- Automotive Industry: Automotive companies segment their market based on factors like income, lifestyle, family size, and driving preferences. They target specific groups such as eco-conscious consumers, families needing spacious SUVs, or luxury buyers. Each vehicle line is then positioned to appeal to its target segment.
- Hospitality Industry: In the hospitality industry, segmentation is based on traveler type, budget, amenities, and purpose of travel. Hotels then target groups like business travelers with work-friendly features or families and couples with leisure-focused offerings. Each property positions itself accordingly. Business hotels as efficient, family resorts as fun and accessible, and luxury stays as premium experiences.
These examples underscore the effectiveness of the STP model in crafting strategies that resonate with targeted audiences and drive business growth.
STP Marketing Examples

Understanding the STP marketing model in theory is one thing, seeing it applied by industry leaders like Nike and Apple brings its power to life.
Both companies have mastered the art of identifying specific market segments, targeting them with precision, and positioning their brands to resonate deeply with their chosen audiences.
Example 1: Nike
Nike's success isn't just about athletic gear, it's about how they connect with their audience through strategic segmentation, targeting, and positioning.

Here's how they do it:
Segmentation by Sport and Lifestyle
Nike segments its market based on various factors:
- Demographics: Age, gender, income level.
- Psychographics: Lifestyle, personality, values.
- Behavioral: Purchasing habits, brand interactions, product usage.
For instance, they differentiate between professional athletes seeking performance gear and casual consumers interested in athleisure wear.
Targeting Fitness-Conscious Youth
Nike focuses on young, fitness-conscious individuals who value both performance and style. This demographic is tech-savvy, socially connected, and seeks brands that align with their active lifestyles.
Positioning as Performance and Empowerment
Nike positions itself as more than just a sportswear brand; it's a symbol of performance, innovation, and empowerment. Their "Just Do It" slogan encapsulates this ethos, encouraging consumers to push their limits.
Example 2: Apple
Apple's approach to the STP model has been instrumental in establishing its brand as a leader in innovation and design.

Segmentation by Tech Proficiency and Premium Preference
Apple segments its market based on:
- Demographics: Age, income, education.
- Psychographics: Lifestyle, values, interests.
- Behavioral: Brand loyalty, usage patterns.
They identify segments that prefer premium, user-friendly technology solutions.
Targeting Creative Professionals
Apple targets creative professionals, such as designers, musicians, and developers, who require powerful, reliable, and aesthetically pleasing devices to enhance their work.
Positioning as Innovative and Sleek
Apple positions its products as the epitome of innovation and sleek design. Their marketing emphasizes simplicity, elegance, and cutting-edge technology, appealing to consumers who value these attributes.
These examples illustrate how the STP marketing model enables companies like Nike and Apple to effectively connect with their target audiences, differentiate their brands, and maintain a competitive edge in their respective markets.
How to Build Your Own STP Marketing Strategy

So far, we've seen how brands like Nike and Apple masterfully use the STP marketing model to carve out space in competitive markets. Now, let's bring that strategy closer to home.
Creating a successful STP strategy isn't rocket science, but it does require data, direction, and a little brand soul-searching.
Tips for Creating Your Marketing STP Process
Before we start, remember this: the STP process in marketing is a loop of discovery and refinement. You segment, target, position, then optimize—and repeat. Here's how to get started and make it stick.
1. Research and Segment Your Market
You can't market to everyone. Trying to appeal to everyone is a shortcut to appealing to no one. Begin with:
- Demographic Segmentation: Age, income, gender, location.
- Psychographic Segmentation: Lifestyle, values, interests.
- Behavioral Segmentation: Purchase patterns, product usage, and brand interactions.
- Geographic Segmentation: City, region, climate, whatever aligns with your product.
Example: If you're selling eco-friendly running shoes, segment your market to identify environmentally conscious consumers who are also active runners aged 25–40 living in urban areas.
Pro Tip: Use tools like Google Analytics, Meta Audience Insights, or market research platforms like Statista to collect this data.
2. Analyze and Select Profitable Targets
Now that you have segments, you need to choose the ones worth pursuing. Ask:
- Which segment has the greatest need for your product?
- Which segment is financially viable?
- Which segment aligns best with your brand values and resources?
Example: From the earlier segmentation, you might decide to focus on millennials who are willing to spend more on sustainable fashion, rather than price-sensitive shoppers.
Focus is your superpower here. Choose the segment(s) that will give you the best ROI and long-term loyalty.
3. Develop a Clear and Unique Brand Position
Your brand position is the mental space you want to own in your customer's mind. It's how you answer the question: "Why should they choose you over the competition?"
To craft this:
- Define what you offer that others don't.
- Express it clearly in your messaging.
- Consistently reinforce it across every channel.
Example: "Our running shoes combine performance with sustainability, designed for runners who care about their footprint, both on the road and on the planet."
The positioning should reflect both emotional and rational benefits to your audience.
4. Tools and Resources for Conducting Marketing STP Analysis
To streamline your STP strategy, consider using tools that help you make informed decisions:
- Google Trends & Google Analytics: For market demand and behavioral insights.
- SEMrush / Ahrefs: For keyword trends and audience search behavior.
- Survey tools like Typeform or SurveyMonkey: To gather direct insights from your target audience.
- CRM platforms like HubSpot or Ringy: To manage and monitor audience engagement through the funnel.
- Canva or Adobe Express: To visually support your brand positioning with consistent design.
Each tool brings a layer of insight that, when combined, helps you execute the STP marketing model with confidence and precision.
With a defined segmentation, a clear target, and a compelling brand position, you're not just "doing marketing"—you're building a strategy that resonates. The STP model gives you the lens to see your audience more clearly and speak to them more meaningfully.
Final Thoughts on STP in Marketing
The STP marketing model is more than a framework, it's the foundation of modern, customer-focused marketing. By understanding how to segment your audience, target the right groups, and position your brand with purpose, you create marketing that actually resonates.
No fluff, no wasted spend, just real, strategic alignment between your brand and your audience.
Whether you're managing campaigns for a global brand or launching your first product, STP helps you cut through the noise with messaging that lands and drives results. It transforms your marketing from broad and bland to focused and effective.
So, what's next?
Start building your own STP marketing strategy today. Dig into your data, identify your most promising segments, and craft a message that speaks directly to them. The clearer your focus, the stronger your impact.
Your move: Use the STP process to sharpen your targeting and clarify your messaging—because the right message, to the right people, always wins.
And if you're ready to take things further, platforms like Ringy can help you streamline this entire process. From segmenting leads and managing campaigns to nurturing customer relationships, Ringy gives you the sales tools to bring your STP strategy to life, all in one place.
Start simple. Stay strategic. And let tech like Ringy do the heavy lifting while you focus on what matters: building meaningful connections.

Skyrocket your sales with the CRM that does it all.
Calling? Check. SMS? Check. Automation and AI? Check. Effortlessly keep in touch with your customers and boost your revenue without limits.

Take your sales to new heights with Ringy.
Sales in a slump? Ringy gives you the tools and flexibility you need to capture leads, engage with them, and turn them into customers.
Subscribe to Our Blog
Enter your email to get the latest updates sent straight to your inbox!
Categories
Related Articles